Human Error in Cybersecurity
A report backed by Anzenna highlights the importance of assessing employee risk through real-time scoring, enabling organizations to prioritize and address vulnerabilities to avert breaches.
Despite implementing numerous security measures to safeguard against cyber threats, the reality remains that human error can easily compromise these defenses. Whether it’s clicking on a malicious link, failing to download the latest updates, or making a configuration error, everyday mistakes can have severe repercussions.
Both individuals and organizations have faced significant repercussions from cyber incidents, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and system outages. Alarmingly, a substantial portion of these incidents could have been averted if not for human oversight.
This article delves into the influence of human mistakes on cybersecurity, offering practical strategies to reduce their impact on personal security and organizational finances.
We’ve gathered compelling statistics, insights, and trends from recent research to illustrate the extent of human error in the realm of cybersecurity.
Public Wi-Fi networks are often rife with vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals exploit unsuspecting users to steal sensitive information like passwords and financial data. It's crucial for anyone accessing public networks to utilize a reliable VPN to secure their internet traffic from prying eyes.
Nevertheless, the Proofpoint 2020 User Risk Report indicates that 45% of American workers mistakenly believe public Wi-Fi is secure when in familiar locations. On a global scale, about 26% of users share this misconception.
Further findings from the same report reveal that over 10% of workers in the UK never secure their smartphones, despite 41% acknowledging that they use their devices for both professional and personal tasks.
Internationally, 42% of survey participants employ biometric locks, such as fingerprint recognition, while 24% rely on a four-digit PIN to secure their devices. Alarmingly, 10% of users have no locking mechanism in place whatsoever.
The Proofpoint report raises additional concerns, noting that 50% of respondents admitted to permitting friends or family to use their work-issued devices. While intentions might be innocent—often to check an email—the risk remains that someone could inadvertently click on a harmful link.
Instances of data breaches often stem from human mistakes, as illustrated by high-profile cases like Equifax and Capital One, as well as New Zealand's gun buyback initiative.
In the Equifax incident, the breach could have been prevented if a staff member had acted on security alerts and carried out the needed software updates.
This issue is not isolated; a 2021 survey by Egress found that a staggering 94% of organizations faced insider data breaches within the previous year. The survey indicated that 84% of IT leaders attributed the majority of these incidents to human error.
Despite this, only 21% of the participants expressed that human error was their primary concern regarding cybersecurity.
Support for these statistics can be found in earlier research by Kaspersky, which in its 2019 report on IT security economics identified “inappropriate use of IT resources by employees” as the leading cause of data breaches. Notably, 50% of small and medium-sized businesses reported encountering such issues.
Human error significantly contributes to cybersecurity vulnerabilities, with various factors at play.
Data indicates that a notable 42 percent of incidents involve the loss of company-owned devices and mobile devices, while 41 percent pertain to lost bring-your-own-device (BYOD) gadgets.
Verizon's 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report offers additional insights, illustrating that phishing emerges as the leading threat action, accounting for over 20 percent of breaches.
Other human-related errors, such as misdelivery and misconfiguration, rank fourth and fifth, each implicated in approximately 10 percent of cases.
Moreover, the report highlights that several primary malware vectors associated with data breaches stem from human mistakes. Email links, downloads containing malware, and email attachments rank first, third, and fourth respectively in their susceptibility.
Interestingly, among the various high-level actions leading to data breaches, human error is the only factor that is consistently on the rise.
Human errors play a significant role in cybersecurity incidents, with the most common types including misconfiguration, misdelivery, and publishing mistakes.
According to Verizon, a striking revelation from the Netwrix 2020 Cyber Threats Report is that over 50% of surveyed employees admitted to disregarding established cybersecurity policies and guidelines.
This behavior may stem from leadership practices; a substantial 85% of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) acknowledged that they relaxed cybersecurity protocols to facilitate remote working for employees.
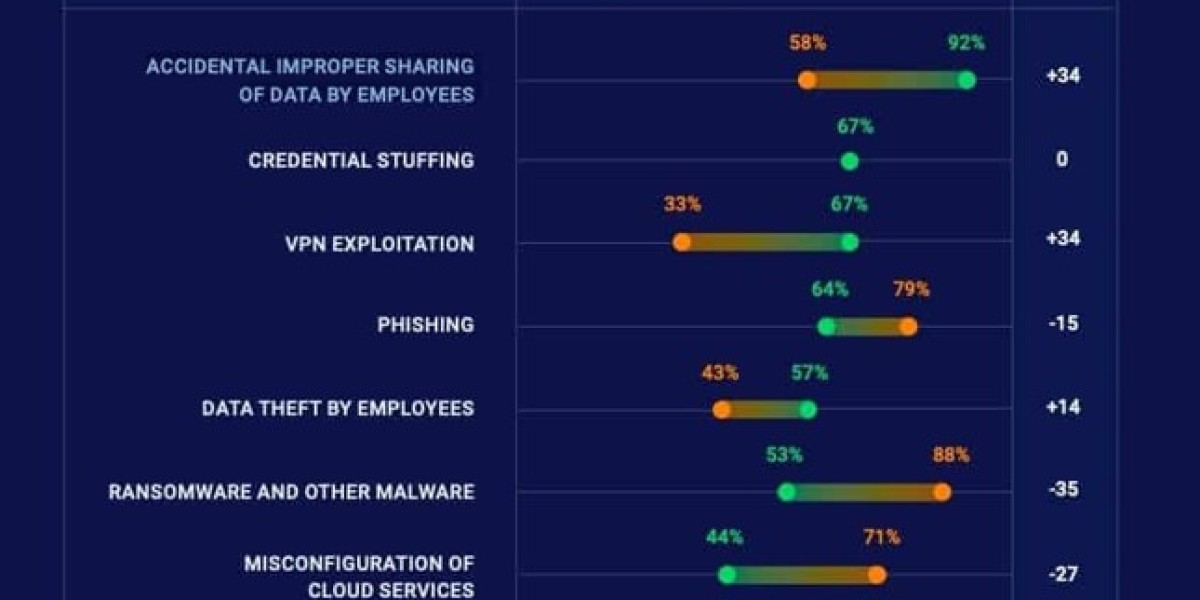
Moreover, the Netwrix report highlights a stark contrast in perceptions of critical threats before and during the pandemic. There was a dramatic rise in the recognition of risks associated with the "accidental and improper sharing of data by employees." Prior to the pandemic, only 58% of organizations viewed this as a critical threat, but this number skyrocketed to 92% in the current landscape.
Human error plays a significant role in the realm of cybersecurity, and recent statistics highlight both the progress made and the ongoing challenges.
For instance, the issue of "misconfiguration of cloud services" has seen a notable decrease in concern, falling from 71% to 44%. Similarly, the frequency of "accidental changes and other mistakes by administrators" has also reduced.
However, the persistence of weak password practices remains alarming. A 2021 study by NordPass, which surveyed 50 countries, revealed that "123456" is still the most commonly used password, with over 103 million users relying on it. This password can be cracked in less than a second. Other common passwords include "123456789," used by 46 million people, "qwerty," utilized by 22.3 million, and "password," which is chosen by 20.9 million users.
The implications of these trends are significant. According to Verizon's 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, a staggering 80% of the 868 hacking incidents analyzed involved compromised passwords. These breaches often occur through lost or stolen credentials or via brute force attacks.
As individuals juggle numerous online accounts—Hypr estimates that many manage over 30—remembering unique passwords can be challenging. This difficulty leads to the widespread practice of password reuse, which poses serious risks. If a password is compromised in a data breach, cybercriminals can employ credential stuffing to exploit that same username-password combination across different accounts.
The prevalence of password reuse is more significant than many might expect. Here are some revealing statistics on this issue affecting both personal and professional accounts:
-
Microsoft reported that 44 million users were guilty of reusing passwords across their accounts.
-
A Google survey found that 13% of users used the same password for every account, while 52% reused passwords across multiple accounts.
-
A survey conducted by Hypr indicated that 72% of participants acknowledged reusing passwords.
-
LastPass discovered that employees often reused passwords across an average of 13 accounts.
-
Furthermore, the Ponemon Institute’s 2020 report on password and authentication security behaviors revealed that IT professionals are the most frequent offenders, with 50% admitting to password reuse compared to 39% among other employees.
These statistics underscore the urgent need for improved password management strategies to mitigate the risks associated with human error in cybersecurity.
A survey conducted by Zebra in 2021 reveals an interesting trend among Americans: a staggering 79% admit to sharing their passwords.
However, despite this high percentage, only a mere 13% express concern regarding the risk of identity theft.
Further analysis from the Ponemon Institute sheds light on the differences in password-sharing habits between IT professionals and the general workforce.
The findings indicate that nearly half (49%) of IT specialists confess to sharing their passwords with coworkers.
This statistic closely mirrors the behavior of non-IT employees, where 51% also report similar practices.
It might seem obvious that changing passwords is essential after a data breach notification, but surprisingly, this isn't the case.
Research by Google indicates that merely 45% of individuals actually take the step to update their passwords following such alerts.
Even more troubling is the Ponemon Institute survey, which reveals that just 65% of IT professionals opt to modify their account protection tactics after experiencing an account compromise. While this does indicate a majority, one would expect a higher figure. In contrast, a more encouraging statistic shows that 75% of the general public would take action in response to a breach.
Have you ever noticed the prevalence of sticky notes plastered around office computers, each displaying various passwords?
This phenomenon is alarmingly common. The Ponemon Institute reports that 42% of organizations depend on this method to help employees access their numerous accounts effectively.
Phishing attacks, while sometimes debated as a form of human error, fundamentally depend on user engagement, often manipulated through social engineering tactics.
Cofense's 2019 phishing report highlighted the importance of awareness training in thwarting these attacks.
For instance, a sophisticated phishing attempt aimed at a prominent healthcare institution was swiftly neutralized within 20 minutes, thanks to vigilant employees who reported the incident.
Despite being frequently overlooked, human error plays a crucial role in cybersecurity challenges.
To combat this, companies worldwide are intensifying their efforts to enhance employee awareness and reduce mistakes.
The global market for cybersecurity training was valued at $1 billion in 2014, with projections by Gartner’s Perry Carpenter estimating it will surge to $10 billion by 2027.
According to the 2020 Netwrix IT Trends Report, a significant focus for organizations is increasing cybersecurity awareness among employees, which was identified as a priority by 52% of respondents. Notably, investment intentions in security awareness have more than doubled for mid-sized companies, rising from 33% to 67% year-over-year.
The shift to remote work during the pandemic has exacerbated cybersecurity vulnerabilities, with Malwarebytes reporting that 20% of organizations faced breaches linked to remote employees.
This statistic emphasizes the human element as a critical risk factor in remote work scenarios.
Working from home often involves personal devices and less secure environments, creating openings for cybercriminals.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must adopt robust cybersecurity strategies, including thorough employee training, secure remote access systems, and comprehensive endpoint protection.
Mitigating Cybersecurity Risks
Ransomware has emerged as one of the most pressing dangers in the realm of cybersecurity.
The financial implications are staggering, with average ransom demands skyrocketing from $812,380 in 2022 to an astonishing $1,542,333 in 2023, as reported by SC Magazine.
This alarming trend underscores the increasing complexity and severity of such attacks.
Additionally, Varonis reported that a staggering 94% of malware is distributed through email, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced email security measures.
To effectively counter the evolving tactics of ransomware, organizations are urged to implement adaptive cybersecurity strategies.
Key measures include conducting regular data backups, deploying sophisticated threat detection systems, and providing comprehensive training for employees to identify and react appropriately to potential threats.
Human error continues to pose a significant risk to cybersecurity.
However, there are strategies that can be employed to mitigate the repercussions of human mistakes within an organization.
While the following suggestions are primarily geared towards businesses, many can also be adapted for personal use at home.
Organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture through various control measures.
One effective approach is applying the principle of least privilege, which restricts employee access to only the data and functionalities necessary for their roles.
This practice significantly reduces the likelihood of sensitive information being compromised or misplaced.
Access control measures can further address risks associated with human errors, such as misdelivery or misconfiguration.
For instance, implementing a policy that requires additional verification on specific tasks ensures that multiple individuals must err before a mistake goes unnoticed.
Password management is another critical area for improvement.
For example, instituting mandatory password changes and enforcing guidelines for password complexity can strengthen security.
Utilizing tools like password strength checkers and strong password generators can be beneficial for this purpose.
Encouraging or mandating the use of password managers for work accounts can also enhance security practices.
Furthermore, employing two-factor authentication (2FA) or two-step verification (2SV) adds an extra layer of protection, safeguarding against weak or shared passwords.
To simplify access for employees, implementing a single sign-on (SSO) system, which allows one password to access multiple accounts, can be advantageous.
Phishing attacks hinge on human participation for success, yet it is also human action that can thwart them.
An essential factor in determining the outcome of such threats is education.
Most cybersecurity awareness training programs are tailored to equip employees with the skills to identify, avoid, and report phishing attempts, ensuring that organizations are prepared for inevitable attacks.
Training initiatives play a crucial role in mitigating human error across various domains like password security, identifying malware, managing data, and ensuring physical safety.
To minimize the risk of falling victim to phishing schemes, organizations can reduce the chances for mistakes. One effective strategy is to mark emails originating from outside the organization distinctly. Additionally, removing hyperlinks from external communications and utilizing sandboxing for attachments can verify their safety prior to accessing them.
Regardless of whether employees utilize company-provided devices or adhere to a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy, it's essential to implement clear guidelines. A straightforward approach is to mandate that all devices are secured with a PIN, passphrase, or biometric authentication.
Moreover, requiring the use of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is vital, especially when employees connect to public Wi-Fi networks. This measure encrypts internet traffic, rendering it unreadable to any potential interceptors. Encouraging or requiring the installation of applications that assist in locating lost or stolen devices, such as Google’s Find My Device or Apple’s Find My app, can be beneficial. Additionally, having the capability to remotely erase devices adds an important layer of security.
To enhance your organization's cybersecurity, consider implementing Mobile Device Management (MDM) or Mobile Application Management (MAM) solutions.
These platforms provide essential functions such as enforcing data encryption, conducting malware scans, remotely wiping data, and tracking devices effectively.
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in our ability to concentrate. A clutter-free and quiet workspace, free from extremes in temperature and humidity, can significantly minimize the likelihood of errors.
Additional factors that can contribute to human mistakes include fatigue from long working hours, overwhelming workloads, privacy concerns, and even improper posture while working.
It's common to adopt a nonchalant approach toward cybersecurity—until a breach occurs. If your organization reacts to threats only after they arise, it's time to foster a proactive culture. Implementing the strategies mentioned can make a difference. Moreover, creating awareness through posters and email reminders about security protocols can reinforce safe practices.
Encouraging open dialogues about cybersecurity is vital. Employees should feel comfortable asking questions or expressing concerns. Remember, cultural change often begins at the top; thus, leadership, particularly those in IT, must model the behaviors they expect from their teams.
Mistakes in cybersecurity are universal and arise from various reasons. Let's explore some frequent issues:
The "Uninformed" Factor: Surprisingly, many individuals lack knowledge regarding online safety. They may be unaware of basic cybersecurity principles or how to navigate common risks.
The "Oops" Factor: Human error is inevitable; people may inadvertently create weak passwords, forget to lock their computers, or click on dubious links.
The "Phishing Trap": Phishing attacks are crafted to mimic legitimate communications, yet they are designed to deceive and capture sensitive information.
The "Software Oversight": Even robust software can harbor vulnerabilities. When employees neglect to update or patch their applications, they leave an opening for cybercriminals to exploit.
By addressing these factors, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of human error in their cybersecurity efforts.Navigating the complexities of technology can often feel overwhelming.
With a multitude of applications, files, and configurations, it’s easy to make a mistake.
A simple slip, like pressing the wrong key or accidentally erasing an important document, can lead to significant issues.
Moreover, high stress and heavy workloads can heighten the likelihood of errors in cybersecurity practices.
When individuals are bogged down with excessive responsibilities and deadlines, maintaining focus on security measures becomes increasingly challenging.
However, there are effective strategies to mitigate human error in the realm of cybersecurity.
Regular training sessions, robust security protocols, and the use of protective tools such as firewalls and antivirus programs play crucial roles.
It's essential to remember that prevention is paramount in ensuring online safety.
Humans, despite being remarkable for our problem-solving abilities and creativity, often represent the weakest point in cybersecurity.
Statistics indicate that more than 90% of cyber incidents stem from human mistakes, such as clicking on malicious links or utilizing weak passwords.
This scenario is akin to leaving your front door ajar, inviting intruders in—only in this instance, the intruders are cybercriminals with malicious intent.
Yet, there’s no need for hopelessness; proactive steps can be taken to minimize the chance of human error.
Education is vital—empower yourself and your team with knowledge about online risks and preventative measures.
Utilizing strong and unique passwords, activating two-factor authentication, and ensuring software is consistently updated are all effective strategies.
Employing common sense is equally important; if something appears suspicious or too good to be true, approach it with caution.
Yes, human error is prevalent in cybersecurity, but equipping yourself with the right tools and understanding can transform you into a vigilant protector against cyber threats.
What is a Netflix VPN and How to Get One
A Netflix VPN is a virtual private network that enables users to access region-restricted content on Netflix by connecting to servers in different countries. By using a Netflix VPN, viewers can bypass geographical limitations and enjoy a wider selection of movies and TV shows available in various regions. To utilize a Netflix VPN, one must choose a reliable VPN provider, install the application, and connect to a server in the region whose content they wish to access.
Why Choose SafeShell as Your Netflix VPN?
If you're looking to access region-restricted content on Netflix, you may want to consider using SafeShell VPN . SafeShell VPN is particularly advantageous for those seeking a reliable netflix unblocked experience due to its high-speed servers that are optimized for seamless streaming. These servers ensure that you can enjoy your favorite shows and movies without any interruptions, offering lightning-fast connection speeds and high-definition streaming capabilities. Additionally, SafeShell VPN allows you to connect up to five devices simultaneously across various platforms such as Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and even Apple TV, making it a versatile choice for multi-device households.
Moreover, SafeShell VPN's exclusive App Mode lets you unlock and enjoy content from multiple regions simultaneously, giving you a diverse range of entertainment options. This feature is complemented by the VPN's lightning-fast speeds, which eliminate buffering and throttling, allowing for smooth streaming, downloading, and browsing experiences. SafeShell VPN also prioritizes your online privacy with its proprietary "ShellGuard" VPN protocol, ensuring top-level security with advanced encryption and robust features to protect your data. With these benefits, SafeShell VPN stands out as a secure and stable choice for unblocking Netflix and exploring global content without restrictions.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Watch Netflix with SafeShell VPN
To begin using SafeShell Netflix VPN , first subscribe to a plan that meets your requirements by visiting the SafeShell VPN website and clicking the "Subscribe Now" button. Once your subscription is active, download and install the SafeShell VPN app on your preferred device, whether it's Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android. After installation, open the app and log in to your account. You'll be presented with two modes; for the best Netflix experience, select the APP mode.
Next, choose a VPN server by browsing the list of available servers. Select a server located in the region whose Netflix content you wish to access, such as the US, UK, or Canada, and then click on "Connect" to establish a connection. Finally, open the Netflix app or visit the Netflix website. Log in to your Netflix account and enjoy streaming the content available in the region you selected using SafeShell Netflix VPN.